Introduction
What Is After-Tax Income? The money still available after deducting federal, state, and withholding taxes is referred to as gross income. What's left over after a person or business has paid their tax debt is "after-tax income," also called "income after taxes." Most people file tax returns using an IRS Form 1040 to calculate their taxable income, the amount of income tax due, and their net income.
One must first deduct expenses from gross income before calculating net income. Take your gross income to start. Taxes must be deducted from the balance because it is the amount that is taxable. Subtract the amount of income tax owed from one's gross income to determine their "after-tax income." Individuals may consider taxes levied by their state and municipal governments when determining their net income. The combined impact of sales tax and property tax when we do this lowers our pre-tax profits.
How After-Tax Income is Calculated
Tax payments are subtracted from gross income to determine after-tax income. For the argument, assume that someone makes $50,000 annually and is subject to a 12% tax rate. An annual tax payment of $6,000 would be required. So this person's income is $44,000 after deductions.
Net income, not gross income, is used to compute corporate after-tax earnings. A corporation reports its annual net profit on its income statement. The amount left over after all expenses have been paid is known as net income. The amount left out after the company has paid taxes after calculating net income is known as after-tax income. An increase in income after taxes can be used to determine profitability.
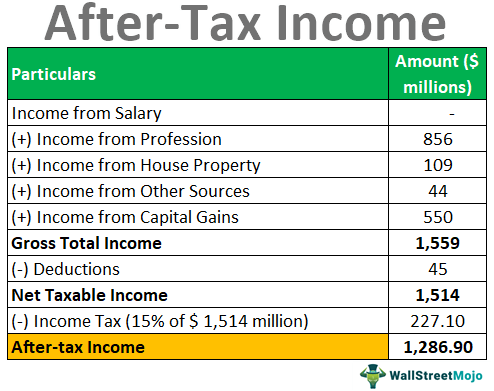
After-Tax Income vs. Before-Tax Income
Before any tax deductions have been made, a taxpayer's total income is referred to as "before-tax income." Even if two individuals make the same amount before taxes, their take-home pay may differ significantly. This is due to individual tax filing status, itemized deductions, and tax credits. If someone else makes the same amount but uses a different method, their after-tax profits can differ from yours. An employee and a business owner could earn the same amount before taxes. Their net earnings, however, may differ dramatically due to the numerous taxes they are subject to.
For instance, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 created the 20% Qualified Business Income Deduction. A solo proprietor would pay tax on 20% less of their income for the same amount produced. Your take-home salary could significantly increase if you add up the possible tax savings.
Net Income After Taxes (NIAT)
Net income after taxes (NIAT) is a term used to indicate a company's financial standing rather than an individual's, similar to the idea of after-tax income. The amount left over after covering all operating costs is known as "net income after taxes." This sum is also referred to as "profit" or "net earnings" (including taxes).
In addition to taxes, operational expenses, interest charges, dividends, and depreciation are subtracted to arrive at net income after taxes. The net income after taxes is one of the most important measures to consider when analyzing a company's financial position. The corporation distributes its earnings to its owners and shareholders after covering all costs. A stronger NIAT almost always results in a better share price for companies listed on public markets.
After-Tax and Pretax Retirement Contributions
Before-tax income is money that will be utilized for things like retirement or other benefits, whereas after-tax income is money that has already been taxed. For example, an employee's take-home pay would be reduced if they contributed to a retirement account before taxes were deducted. After deducting these from your gross salary, your employer will determine your payroll taxes.
After deducting the residual amount from the gross wage, the remaining money is utilized to compute Social Security and Medicare contributions. Suppose an employee chooses to fund their retirement from income that has already been taxed. In that case, the employer will first take taxes from the employee's gross compensation before deducting the retirement contributions. This is because the company is required by law to do so.

Conclusion
When an employee has a deduction taken out of their paycheck after taxes, the money is taken out of their paycheck after taxes have already been deducted. The portion of a paycheck that remains after all obligatory deductions, such as payments to social security and income taxes paid to the federal and state governments, have been taken out. Although the after-tax revenues that businesses get through digital transactions are analogous to those of people, businesses often begin by estimating total revenues rather than looking at gross income. They begin by determining how much money is available after deducting taxes.